Welding Vs. Soldering: A Comprehensive Comparison
Welding versus soldering – which one should you choose for your next project? Well, the answer depends on a few factors. If you’re unfamiliar with these two processes, allow me to shed some light. Welding involves joining two or more pieces of metal by melting them together, creating a strong and permanent bond. On the other hand, soldering is a technique used to join objects together by melting a filler metal, known as solder, and then cooling it to form a connection. Both methods have their unique applications and advantages, and in this article, we’ll explore the differences between welding and soldering to help you make an informed decision. So, let’s dive in, shall we?
Welding Versus Soldering
The Basics of Welding and Soldering
Welding and soldering are two distinct methods used to join pieces of metal together. While they serve the same purpose, there are key differences in their techniques, applications, and the strength of their resulting bonds.
Welding is a process that involves melting the base metal pieces together, allowing them to fuse and form a strong bond. It is commonly used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries, where durability and structural integrity are crucial.
Soldering, on the other hand, involves melting a filler metal (solder) to join two metal surfaces together. Solder typically has a lower melting point than the base metals being joined, making it suitable for electronic and electrical applications, such as circuit boards and jewelry making.
Strength and Durability
When it comes to strength and durability, welding typically provides a stronger bond compared to soldering. The fusion of metals during welding creates a bond that is capable of withstanding heavy loads and structural stresses. It is commonly used in applications where the joint needs to remain intact under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, pressure, or vibrations.
Soldering, on the other hand, creates a weaker bond due to the lower melting point of solder compared to the base metals. While soldered joints are generally sufficient for less demanding applications, they may not hold up well under heavy loads or extreme conditions.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of your project when deciding between welding and soldering. If strength and durability are essential, welding is likely the better choice. However, if the joint will not be subjected to excessive stress or harsh conditions, soldering may be a suitable and more cost-effective option.
Application Differences
Welding and soldering have distinct applications where they excel. Understanding these differences can help you determine which method is most appropriate for your project.
Welding Applications
- Construction: Welding is widely used in the construction industry for joining structural steel, pipelines, and heavy machinery.
- Automotive: Welding plays a crucial role in automobile manufacturing and repairs, such as joining car frames and repairing exhaust systems.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry relies on welding for fabricating aircraft bodies, engine components, and other critical parts.
- Manufacturing: Welding is essential in various manufacturing processes, including metal fabrication, assembly line production, and welding-based machining.
Soldering Applications
- Electronics: Soldering is extensively used for assembling electronic components on circuit boards, creating connections between wires, and repairing electronic devices.
- Jewelry Making: Soldering is a common technique in jewelry making for connecting metal pieces, attaching clasps, and setting gemstones.
- Plumbing: Soldering is often employed in plumbing applications, including joining copper pipes and fittings.
- Arts and Crafts: Soldering finds uses in various artistic endeavors, such as stained glass artwork and metal sculpture.
Equipment and Techniques
Both welding and soldering require specific equipment and techniques to achieve successful results. Let’s explore their differences.
Welding Equipment and Techniques
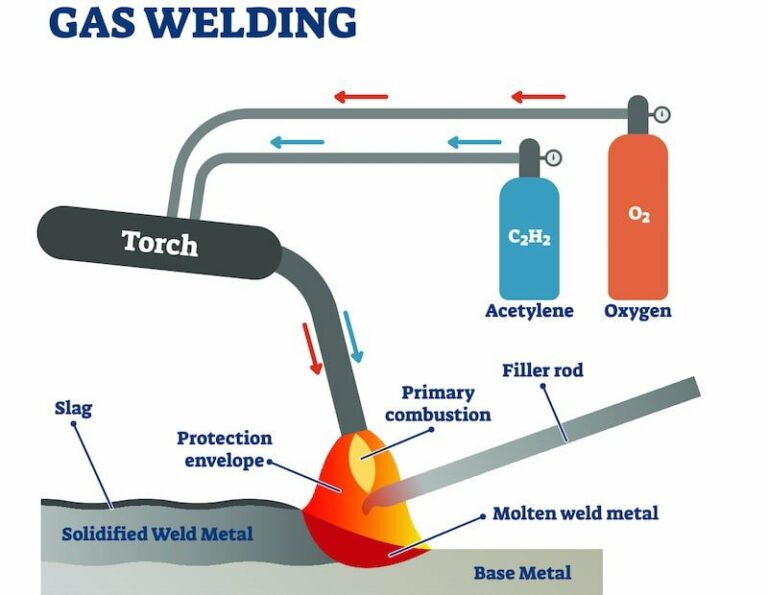
Welding involves the use of high-temperature heat sources, such as arc welding, gas welding, or laser welding. The process requires electricity or fuel gases to generate the necessary heat for melting the base metals. Protective gear, including welding helmets, gloves, and welding curtains, is essential to ensure safety during welding.
The welding technique varies depending on the type of welding being performed. Common welding techniques include:
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
- Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
- Resistance Spot Welding (RSW)
Soldering Equipment and Techniques
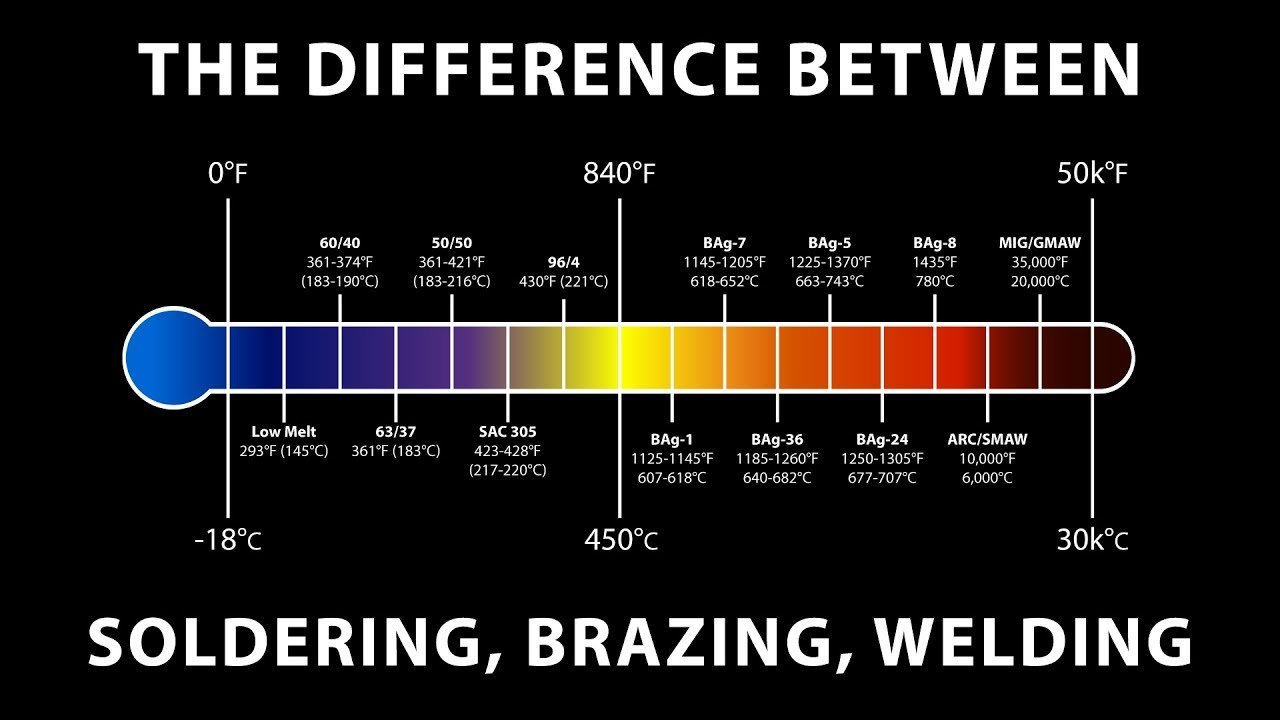
Soldering requires a soldering iron or soldering gun, solder wire, and flux. The flux helps remove oxidation from the metal surfaces, allowing the solder to flow and create a strong bond. Unlike welding, soldering operates at lower temperatures, typically below 450 degrees Celsius (840 degrees Fahrenheit).
Common soldering techniques include:
- Through-Hole Soldering
- Surface Mount Soldering
- Desoldering
- Reflow Soldering
Cost Considerations
The cost of welding and soldering varies depending on several factors, including the equipment, materials, and complexity of the project.
Welding can be more expensive due to the need for specialized welding machines, consumables, and safety equipment. Additionally, the expertise required for welding may result in higher labor costs when hiring professional welders.
Soldering, on the other hand, is generally more affordable in terms of equipment and materials. Soldering irons and solder wires are relatively inexpensive, making it an accessible joining method for DIY enthusiasts and small-scale projects.
When determining the cost-effectiveness of welding versus soldering, consider the scale of your project, the materials involved, and the desired strength and durability of the joint. Assessing these factors will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and requirements.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
When deciding between welding and soldering, consider the following factors:
Strength Requirements
If your project involves heavy loads, structural components, or the need for joints to withstand extreme conditions, welding is likely the better choice due to its superior strength and durability.
Application
Consider the specific application of your project. Welding is commonly used in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries, while soldering finds extensive applications in electronics, jewelry making, and smaller-scale projects.
Materials
Take into account the types of materials being joined. Welding is suitable for various metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Soldering is primarily used for joining metals with lower melting points, like copper, brass, and tin.
Cost
Assess your budget and project scale. Welding may require greater investment in terms of equipment, consumables, and professional expertise. Soldering is generally more cost-effective for smaller projects and DIY applications.
Experience and Expertise
Consider your level of experience and available expertise. Welding often requires training and certification to ensure safe and effective execution. Soldering, on the other hand, can be learned and performed by DIY enthusiasts with proper precautions.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most appropriate method for your project and achieve the desired results.
The Difference Between Soldering, Brazing, and Welding – Solder Series: Ep. 2
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between welding and soldering?
Welding and soldering are both methods used to join pieces of metal together, but they differ in terms of technique and application. Welding involves using high heat to melt and fuse the metals together, creating a strong and permanent bond. On the other hand, soldering uses lower heat and a filler metal (solder) with a lower melting point, which forms a bond by adhering to the surface of the metals. This bond is typically less strong than a welded joint and is commonly used for electrical and plumbing connections.
Which method, welding or soldering, is stronger?
Welding generally produces stronger joints compared to soldering. The high heat generated in welding allows the metals to melt and fuse together, resulting in a robust joint that can withstand heavy loads and stress. Soldering, on the other hand, creates a weaker joint as the metal pieces are not melted and fused together. The strength of soldered joints is typically limited to the strength of the solder material itself, which may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
When should I use welding instead of soldering?
Welding is preferred when a strong, permanent joint is necessary. It is commonly used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive where the joints need to withstand heavy loads, vibrations, and harsh environments. Welding is ideal for joining thick metal pieces or dissimilar metals that require a high-strength bond. Additionally, welding is suitable for structural applications where the joint integrity and durability are crucial.
When is soldering a better choice than welding?
Soldering is often used when a temporary or less robust joint is required. It is commonly employed in electrical and electronics applications to connect wires, circuit boards, and delicate components. Soldering is also useful for low-temperature materials that cannot withstand the high heat of welding without damage. The ability to create precise and neat joints along with the ease of disassembly makes soldering preferable in situations where repair or modification may be necessary.
Can you solder and weld the same materials?
Typically, the materials suitable for soldering and welding overlap, but some materials may be more compatible with one method than the other. While both processes can join metals such as steel, copper, and aluminum, certain factors like thickness and surface condition may influence the choice. Welding is generally more versatile in terms of material compatibility and can handle a broader range of metal thicknesses and conditions. It is important to consider the specific properties of the materials being joined to determine whether soldering or welding is the most appropriate method.
Is soldering easier to learn than welding?
Soldering is generally considered easier to learn and master compared to welding. Soldering requires less equipment and lower heat, making it more accessible for beginners. The soldering process itself is relatively simple, involving the application of heat to melt the solder and create a connection. Welding, on the other hand, requires specialized equipment, training, and practice to achieve proper techniques and ensure strong welds. However, both soldering and welding skills can be developed with practice and experience.
Final Thoughts
Welding and soldering are both widely used techniques in joining metals and other materials. While welding involves melting and fusing the base metals together, soldering uses a lower-temperature filler material to create the bond.
In conclusion, the choice between welding and soldering depends on the specific requirements of the project. Welding is ideal for creating strong, permanent connections, especially in heavy-duty applications. On the other hand, soldering is better suited for delicate electronics or situations where heat can be detrimental. Both techniques have their merits and should be carefully considered based on the desired outcome. Understanding the differences between welding and soldering allows for informed decision-making in various industrial and DIY projects.