How To Weld Metal Pipes
Today we discuss How To Weld Metal Pipes. Welding metal pipes requires precision, patience, and a keen understanding of the materials and tools involved. With the right techniques and a systematic approach, you’ll be able to join metal pipes seamlessly, creating strong and reliable connections that withstand the test of time. Whether you’re working with steel, stainless steel, or other alloys, we’ll cover the fundamental principles that apply to all pipe welding projects. So, grab your safety gear, and let’s get started on this exciting journey of mastering the art of welding metal pipes!
How to Weld Metal Pipes:
- Prepare the pipes by cleaning the surfaces and removing any rust or paint.
- Choose the appropriate welding technique, such as TIG or MIG welding.
- Set up your welding machine according to the pipe material and thickness.
- Secure the pipes in position using clamps or a vise.
- Start welding by creating a tack weld to hold the pipes together.
- Continue welding along the joint, using a steady and consistent motion.
- Inspect the weld for any defects and make necessary adjustments.
- Clean the welded area and remove any slag or spatter.
- Apply a protective coating or paint, if desired.

How to Weld Metal Pipes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Welding metal pipes is a crucial skill for anyone involved in construction, plumbing, or metalworking. Whether you need to join two pipes together or repair a damaged section, knowing how to weld pipes properly is essential. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process step by step, ensuring that you have all the information you need to weld metal pipes effectively and safely.
Step 1: Prepare Your Work Area
Before you begin welding, it’s important to set up your work area properly. Start by ensuring that you have adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes. Clear any flammable materials from the vicinity and have a fire extinguisher nearby as a precaution.
Next, clean the pipes thoroughly to remove any dirt, grease, or rust that may interfere with the welding process. Use a wire brush or sandpaper to achieve a clean and smooth surface.
Once the pipes are clean, secure them in a stable position using clamps or a vise. This will prevent any movement during the welding process, ensuring accurate and precise welds.
Additionally, make sure you have all the necessary safety equipment, including welding gloves, a welding helmet with a face shield, and protective clothing.
Step 2: Set Up and Adjust Your Welding Equipment
Now that your work area is ready, it’s time to set up and adjust your welding equipment. Start by selecting the appropriate welding method for your specific project.
Common methods used for welding metal pipes include stick welding, MIG welding, and TIG welding. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, so choose the one that suits your needs best.
Next, adjust your welding machine according to the specifications of the metal pipes you are working with. This includes setting the correct amperage, wire feed speed, and gas flow rate if applicable.
Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or seek guidance from an experienced welder if you are unsure about the optimal settings. Proper adjustment of your welding equipment is essential to achieve strong and durable welds.
Step 3: Execute the Welding Process
With your work area prepared and your welding equipment set up, it’s time to start the welding process. Begin by striking an arc between the welding electrode or wire and the base material.
Hold the electrode at a slight angle to the joint and maintain a steady hand motion as you move along the joint. This will ensure consistent penetration and fusion between the pipes.
As you weld, pay attention to the welding puddle and the color of the arc. The puddle should be fluid and evenly distributed, while the arc should have a steady and uniform appearance. Adjust your welding technique and parameters as needed to achieve the desired results.
Remember to maintain a consistent travel speed and avoid excessive heat buildup, as this can lead to distortion or burn-through of the pipes.

Step 4: Post-Welding Inspection and Finishing
After completing the welding process, it’s crucial to inspect the welds for quality and integrity. Look for any signs of porosity, cracks, or incomplete fusion, as these can compromise the strength and durability of the joint.
Use non-destructive testing methods such as visual inspection, dye penetrant testing, or radiographic testing if necessary.
If the weld passes the inspection, you can proceed with finishing the joint. Use a wire brush or grinder to remove any excess weld material and achieve a smooth surface.
This will not only improve the appearance of the weld but also ensure proper fitment if additional piping or fittings need to be connected. Finally, clean the weld area to remove any debris, and apply a suitable protective coating if required.
Step 5: Practice and Continual Improvement
Welding metal pipes is a skill that requires practice and experience to master. The more you weld, the better you’ll become at producing high-quality and reliable welds.
Take the time to learn from your mistakes and seek feedback from experienced welders. Continually refine your welding technique and stay updated with the latest industry practices and advancements.
With dedication and perseverance, you’ll become a proficient pipe welder in no time.
Faqs for How To Weld Metal Pipes:
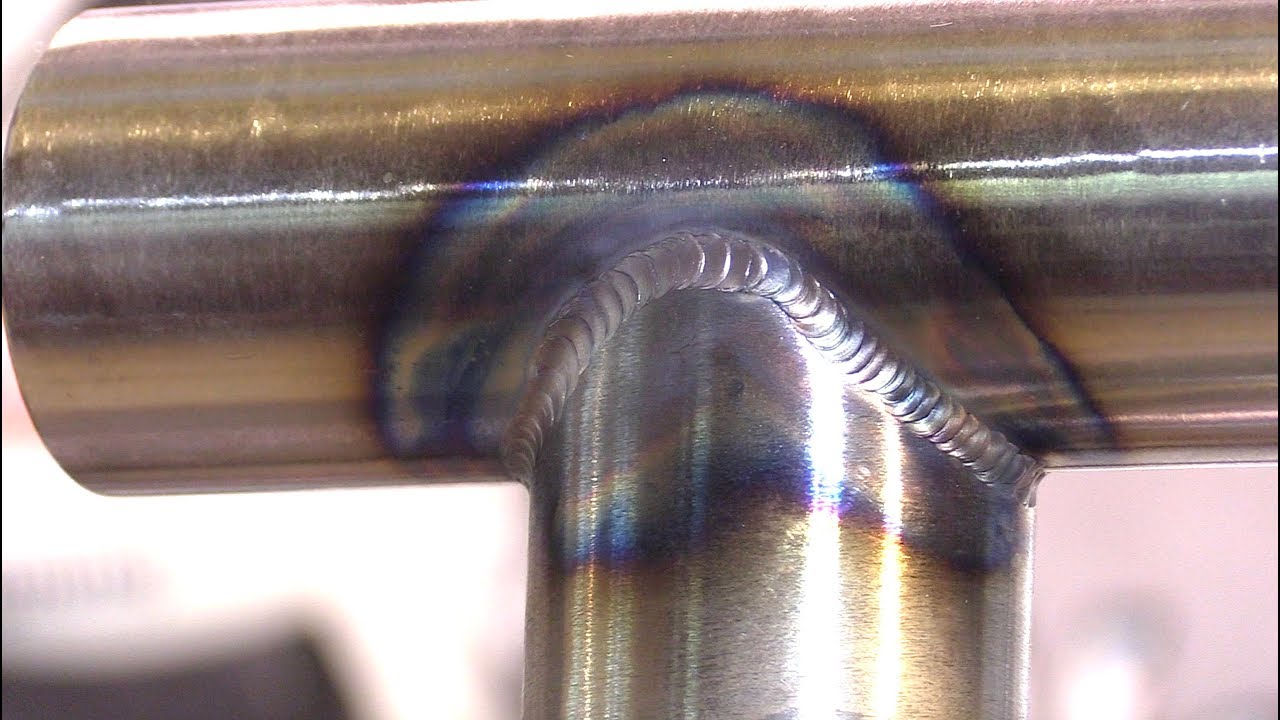
When it comes to welding metal pipes, the most commonly used welding process is Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding. TIG welding offers precise control over the heat input and produces high-quality welds. It is particularly suitable for welding stainless steel and other non-ferrous metals. TIG welding provides excellent weld bead appearance and minimizes the risk of contamination, making it the preferred choice for many pipe welding applications.
However, other welding processes like Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) or Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) can also be used depending on the specific requirements of the project. It is important to consider factors such as the type of metal, pipe diameter, and joint configuration when selecting the appropriate welding process.
Welding metal pipes involves working with high temperatures and potentially hazardous materials. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize safety during the welding process. Here are some essential safety precautions to follow:
1. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as welding gloves, safety glasses, and a welding helmet with a proper shade level to protect your eyes and face from UV radiation.
2. Ensure proper ventilation in the welding area to prevent the accumulation of toxic fumes and gases. If welding in a confined space, use an air-supplied respirator.
3. Securely clamp or hold the pipes in place to prevent movement during welding, reducing the risk of weld defects or accidents.
4. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and remove any flammable materials from the welding area.
5. Follow proper electrical safety procedures and inspect the welding equipment regularly for any damage or malfunction.
The recommended welding technique for welding metal pipes is the “backstep” or “staggered” welding technique.
This technique involves welding small sections of the joint at a time, starting from the end and gradually working your way toward the root of the joint.
By doing so, you allow the previously welded sections to cool down, minimizing the risk of distortion and ensuring proper fusion between the metal pipes.
When using the backstepping technique, it is essential to maintain a steady travel speed and control the heat input to achieve uniform penetration and prevent burn-through.
Additionally, be sure to clean the weld joint thoroughly before starting the welding process to remove any contaminants that could compromise the quality of the weld.
While welding metal pipes, several defects can occur that may compromise the integrity and strength of the weld. It is crucial to be aware of these defects and take necessary measures to avoid them. Some common defects to watch out for include:
1. Lack of fusion: This occurs when the weld metal fails to fuse completely with the base metal or previous weld pass. It can lead to weak joints and potential leakage.
2. Porosity: Porosity refers to the presence of gas pockets or voids in the weld metal. It weakens the weld and makes it susceptible to corrosion and cracking.
3. Cracking: Cracks can occur in the weld metal due to various factors such as excessive heat, rapid cooling, or high levels of residual stress. Cracks compromise the structural integrity of the weld and can lead to failure.
4. Undercutting: Undercutting is the groove-like depression formed along the edges of the weld. It weakens the joint and increases the risk of stress concentration.
To achieve high-quality welds on metal pipes, follow these tips:
1. Prepare the pipe and joint properly by cleaning off any dirt, oil, or rust. Use suitable cleaning methods such as wire brushing, grinding, or chemical cleaning.
2. Choose the correct filler metal that matches the base metal to ensure proper fusion and mechanical properties of the weld.
3. Maintain a consistent arc length and travel speed throughout the welding process to achieve uniform penetration and weld bead appearance.
4. Use proper shielding gas or flux to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, such as oxidation or nitrogen absorption.
5. Post-weld treatment, such as stress relief annealing or heat treatment, may be necessary for certain applications to reduce residual stresses and improve the weld’s mechanical properties.
Source: ytimg.com
Conclusion:
learning how to weld metal pipes is a valuable skill that can open up a world of possibilities in various industries. Whether you’re interested in pursuing a career as a welder or simply want to tackle some DIY projects at home, mastering this technique will undoubtedly prove to be beneficial. By following the proper safety precautions, understanding the different types of welding techniques, and practicing regularly, you can become proficient in welding metal pipes.
Remember, welding is not just about joining two pieces of metal together, but it is an art form that requires precision, patience, and attention to detail. As you embark on your journey to become a skilled welder, do not be discouraged by initial challenges but embrace them as opportunities for growth and improvement. With time and dedication, you will gain confidence in your abilities and be able to tackle more complex projects with ease.
So, go ahead and dive into the fascinating world of welding metal pipes. Whether you’re working on a construction site, building a custom-made structure, or simply repairing household items, the knowledge and skills you acquire will serve you well throughout your life. Happy welding!


