Mig Welding Basics
If you’re eager to dive into the world of welding, you’ve come to the right place! In this guide, we’re going to explore the ins and outs of MIG welding basics. So, what exactly is MIG welding? Well, it’s a popular welding technique that stands for Metal Inert Gas welding, and it’s widely used in various industries.
With MIG welding, you can join metals together by creating an electric arc between the workpiece and a consumable wire electrode. This process generates intense heat, melting the metal and creating a strong, lasting bond. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your welding skills, understanding the basics of MIG welding is essential for mastering this art.
Ready to embark on this exciting journey where sparks fly, and metal bonds are formed? Let’s begin by exploring the fundamental principles of MIG welding, step by step. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation and the confidence to tackle your own welding projects. So put on your safety gear and let’s get started!
Master the art of MIG welding with this step-by-step tutorial. No more confusion! Follow these simple steps to become a welding pro:
Step-by-Step Guide:
– Set up your MIG welder and safety equipment.
– Prepare the metal and clean the surface.
– Adjust the wire feed and voltage settings.
– Hold the gun at the correct angle and distance.
– Start welding and maintain a steady pace.
With these fundamental MIG welding basics, you’ll be well on your way to creating impressive welds. Happy welding!
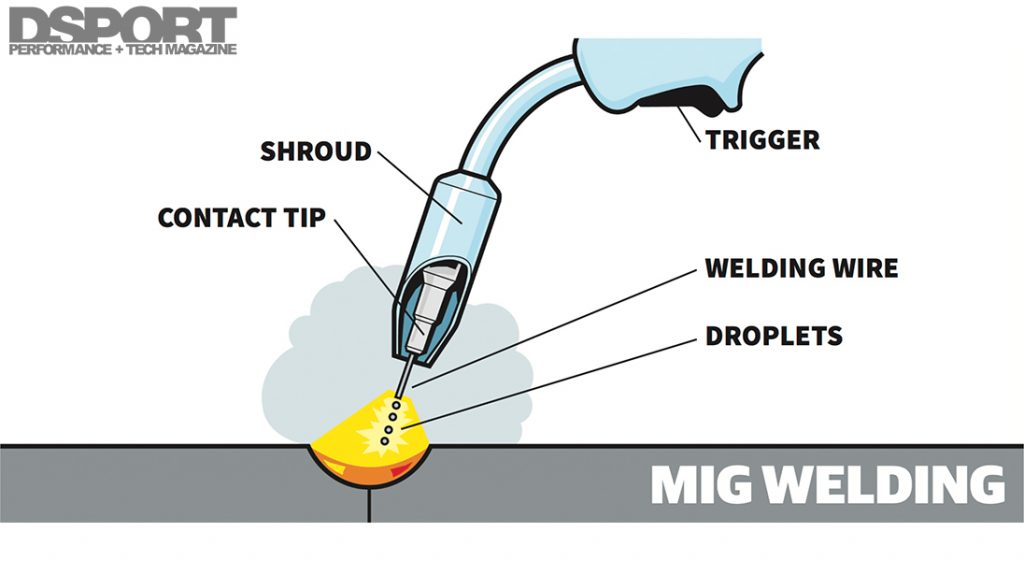
MIG Welding Basics: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to joining and fabricating metal, MIG welding is one of the most widely used and versatile processes. MIG, short for Metal Inert Gas, is a type of arc welding that utilizes a consumable wire electrode and an inert gas to create strong and durable welds. Whether you’re a beginner looking to learn the basics or an experienced welder seeking a refresher, this article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to MIG welding basics.
The Advantages of MIG Welding
MIG welding offers a range of advantages, making it a popular choice for professionals and hobbyists alike. First and foremost, MIG welding is known for its versatility. It can be used to weld a wide variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel. Additionally, MIG welding is relatively easy to learn and master, making it accessible to individuals with varying levels of experience.
Another key advantage of MIG welding is its efficiency. The process allows for high welding speeds, resulting in increased productivity. Furthermore, MIG welding produces clean and aesthetically pleasing welds, making it ideal for applications where appearance is important. Finally, MIG welding is known for its strong and durable welds, providing excellent mechanical properties and structural integrity.
MIG Welding Equipment: The Essentials
Before diving into the world of MIG welding, it’s important to understand the equipment required for the process. The essential components of MIG welding equipment include the power source, welding gun, shielding gas, wire feed mechanism, and welding wire.
The power source is responsible for providing the necessary electrical current to create the arc. It can either be a transformer-based or an inverter-based unit. The welding gun, also known as the MIG torch, is held by the welder and is used to control the wire feed and the flow of shielding gas. The shielding gas, typically a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, is crucial for protecting the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. The wire feed mechanism feeds the consumable welding wire, which serves as the electrode, through the welding gun and into the weld pool.
When it comes to selecting the welding wire, it’s important to consider factors such as the type of metal being welded and the desired characteristics of the weld. Different types of welding wire are available, including solid wire, flux-cored wire, and metal-cored wire, each with its own unique properties and applications.
The MIG Welding Process: Step-by-Step
Now that you’re familiar with the equipment, let’s dive into the MIG welding process itself. The following steps outline a typical MIG welding procedure:
- Prepare the work surface: Begin by cleaning the surface of the metal to be welded, removing any dirt, rust, or other contaminants that may interfere with the weld quality.
- Set up the equipment: Ensure that the power source is properly connected and set the appropriate welding parameters such as wire speed, voltage, and shielding gas flow rate.
- Position the welding gun: Hold the welding gun at a 15-45 degree angle, with the tip approximately ⅜ inch from the work surface.
- Initiate the arc: Depress the trigger on the welding gun to initiate the arc. This will simultaneously start the flow of shielding gas and feed the welding wire into the weld pool.
- Control the weld pool: Move the welding gun along the joint, maintaining a consistent travel speed to ensure proper fusion. Control the size of the weld pool by adjusting the wire feed and voltage settings as needed.
- Monitor the weld quality: Pay attention to the appearance of the weld, looking for signs of proper penetration and fusion. Adjust the welding parameters if necessary.
- Finish the weld: Once the desired length of the weld is achieved, release the trigger to stop the flow of shielding gas and the wire feed. Allow the weld to cool naturally before handling.
Key Tips for Successful MIG Welding
While understanding the MIG welding process is essential, implementing certain tips and best practices can significantly improve the quality of your welds. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
- Properly prepare the work surface by removing any contaminants.
- Maintain a consistent travel speed and arc length for uniform welds.
- Use the correct welding technique, such as a push or pull technique, depending on the metal being welded.
- Ensure proper gas coverage by positioning the welding gun at the correct angle and maintaining an appropriate shielding gas flow rate.
- Choose the right welding wire for the specific application to achieve desired weld characteristics.
- Practice proper safety precautions, such as wearing appropriate protective gear and working in a well-ventilated area.
MIG Welding vs. Other Welding Processes
While MIG welding has its advantages, it’s important to understand how it compares to other common welding processes. Here’s a brief comparison of MIG welding with TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding and Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW):
| Aspect | MIG Welding | TIG Welding | Stick Welding (SMAW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast | Medium | Slow |
| Ability to Weld Different Metals | High | High | Medium |
| Weld Appearance | Good | Excellent | Fair |
| Complexity | Low | High | Low |
As shown in the table, MIG welding offers fast welding speeds, good weld appearance, and the ability to weld a wide range of metals. TIG welding, on the other hand, provides excellent weld appearance and is ideal for applications that require the utmost precision. Stick welding is known for its simplicity and suitability for outdoor and rough working conditions. Ultimately, the choice of welding process depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of the project at hand.
Essential Safety Precautions
When engaging in any welding process, safety should always be a top priority. Here are some essential safety precautions to keep in mind while MIG welding:
- Wear appropriate protective gear, including a welding helmet, gloves, and a flame-resistant jacket.
- Ensure good ventilation in the work area to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes and gases.
- Protect yourself and others from welding sparks and molten metal by using welding screens or curtains.
- Avoid welding near flammable materials or in environments with combustible gases.
- Inspect the welding equipment regularly to ensure proper functioning and prevent accidents.
Common MIG Welding Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced welders can make mistakes. Recognizing common MIG welding mistakes and knowing how to avoid them can help you produce high-quality welds. Here are some frequently encountered mistakes and their solutions:
Inadequate penetration:
This can occur when the welding current is too low or the travel speed is too high. Adjust the welding parameters to ensure adequate heat input and slower travel speed.
Burn-through:
Burn-through happens when the welding current is too high or the travel speed is too slow. Reduce the welding current or increase the travel speed to prevent excessive heat buildup.
Excessive spatter:
Spatter refers to the metal particles that detach from the weld and can lead to a messy work environment. To reduce spatter, select the appropriate wire feed speed, shielding gas flow rate, and welding technique.
Poor weld appearance:
Aesthetics are important in certain applications. Achieving a good weld appearance requires careful control of the welding parameters, including the voltage, wire feed speed, and travel speed. Practice and experimentation can also help improve weld appearance over time.
Expanding Your Knowledge of MIG Welding
Now that you have a solid understanding of MIG welding basics, consider expanding your knowledge by exploring more advanced techniques and applications. Continuously seeking new knowledge, practicing regularly, and learning from experienced welders can help you become a skilled and proficient MIG welder. Remember to prioritize safety and never stop learning!
Key Takeaways: MIG Welding Basics
- MIG welding is a type of welding process that uses a continuous wire electrode and a shielding gas.
- It is commonly used for welding metals like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
- The equipment needed for MIG welding includes a welding machine, wire feeder, welding gun, and gas cylinder.
- Proper safety precautions, such as wearing protective gear and working in a well-ventilated area, should always be followed when MIG welding.
- Mastering the technique of MIG welding requires practice and understanding the importance of maintaining the correct parameters, such as wire speed and voltage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on MIG welding basics. Here, we answer some common questions related to the fundamentals of MIG welding. Whether you’re a beginner or just looking to refresh your knowledge, these questions will provide you with the information you need to get started or improve your skills.
1. What is MIG welding and how does it work?
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a process that uses a continuous wire electrode (the “filler wire”) to join two pieces of metal together. The wire is fed through a welding gun, which also emits a shielding gas to protect the weld puddle from atmospheric contamination. When the wire comes into contact with the metal being welded and an electrical current is passed through it, an arc is created, melting the wire and the base metal. The molten metal then cools and solidifies, forming a strong bond between the two pieces.
MIG welding is favored for its ease of use, versatility, and ability to achieve high welding speeds. It can be used on a variety of metals, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
2. What are the advantages of MIG welding?
MIG welding offers several advantages over other welding processes. Firstly, it is relatively easy to learn, making it a popular choice for beginners. The continuous wire feed allows for longer welds without the need to stop and replace electrodes, increasing productivity. Additionally, MIG welding produces clean and aesthetically pleasing welds, requiring minimal post-weld cleanup. The process also allows for greater control of heat input, reducing the risk of distortion or warping in the metal being welded.
Furthermore, MIG welding can be used in a variety of positions and applications, from thin sheet metal to heavy structural steel. It offers good penetration and can weld a wide range of metal thicknesses.
3. What equipment do I need for MIG welding?
To get started with MIG welding, you will need a few essential pieces of equipment. The most important component is a MIG welding machine, also known as a welder or power source. This machine generates the electrical current needed for the welding process. You will also need a welding gun or torch, which holds and guides the welding wire. The gun is connected to the welding machine via a cable.
In addition, you will require shielding gas, which protects the weld puddle from atmospheric contamination. Common shielding gases used in MIG welding include argon, carbon dioxide, and a mixture of the two. A gas regulator is used to control the flow and pressure of the shielding gas. Lastly, you will need a supply of welding wire, which is selected based on the type of metal being welded.
4. How do I prepare the metal for MIG welding?
Proper preparation of the metal is crucial for achieving quality welds in MIG welding. Start by cleaning the metal surface to remove any contaminants, such as dirt, oil, grease, or rust. It is recommended to use a wire brush or grinder to clean the area to be welded. Remove any paint or coatings as well.
Next, ensure that the metal pieces are properly aligned and securely clamped together. This will prevent any movement during the welding process, ensuring that the joint is well-formed. It is also essential to create a beveled edge or groove on the joint to increase the surface area and enhance the strength of the weld. The specific bevel angle and dimensions will depend on the metal thickness and joint design.
5. What are some common mistakes to avoid in MIG welding?
While MIG welding is relatively straightforward, there are a few common mistakes that beginners should be aware of and avoid. One mistake is improper wire feeding, which can lead to inconsistent welds or burnback, where the wire fuses to the contact tip.
Another mistake is welding too fast or too slow. Welding too fast can result in a weak or incomplete weld, while welding too slow can create excessive heat and lead to distortion or burn-through. It is important to maintain a steady travel speed to achieve proper penetration and bead appearance.
Poor shielding gas coverage is another mistake to avoid. Insufficient shielding gas can cause porosity in the weld, weakening its strength. Ensure adequate gas flow and proper positioning of the welding gun to achieve good gas coverage.
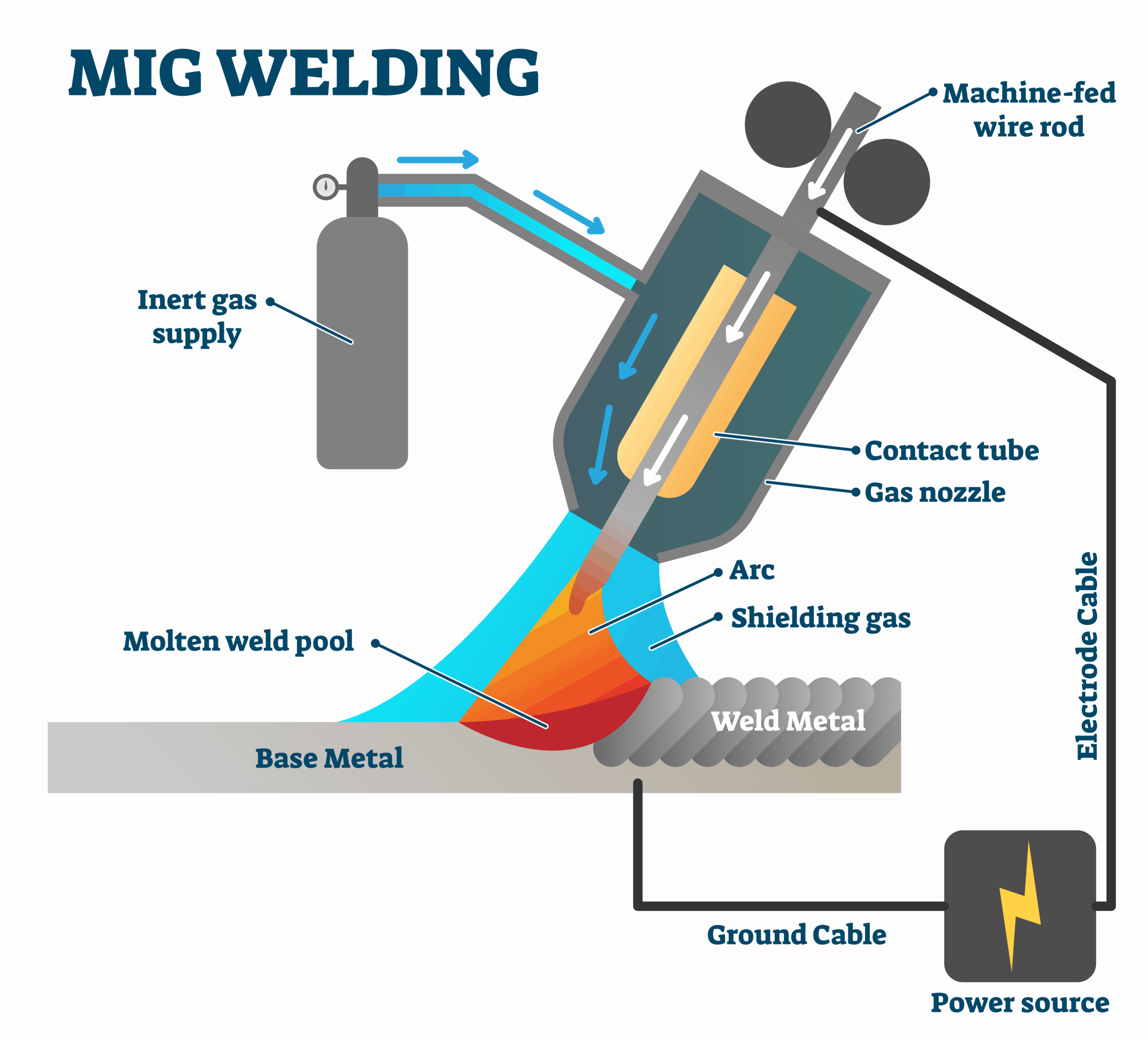
Summary
So, to sum it all up, MIG welding is a process that uses electricity to join metal parts together. It’s like using a hot glue gun, but with metal instead of glue. By feeding a wire electrode through a welding torch, you can create an electric arc that melts the wire and the two metal pieces, forming a strong bond. MIG welding is great for beginners because it’s easy to learn and offers a lot of control. Just remember to wear safety gear and practice proper techniques to ensure a successful weld.
In conclusion, MIG welding is a versatile and accessible method for joining metal parts. With the right equipment, safety precautions, and practice, anyone can become a skilled MIG welder. So go ahead, grab that welding torch, and let your welding journey begin!